Significant Dissimilarities between Flexible Circuit and Rigid Circuit
Differences Between Flexible Circuit and Rigid Circuit
Printed circuit boards (PCBs) are indispensable modules in electronic devices. Comprising fuse, resin, and conductive metal regulate electricity flow with special wiring in electronic components to form a complete and purposeful unit. Whereas all circuit boards instinctively execute the same straight job for the electronic components, their structure's design and constituents are tailor-made due to their use in particular applications. Most circuit boards integrate two significant circuitries, namely a flexible circuit board and a rigid circuit board to connect electronic components in various consumer and industrial appliances.

Flexible Circuit
The flex circuit board is a delicate and thin conductive strip of copper attached to a dielectric film generally polyimide. It allows the board to bend into different angles without any mutilation and withstand shock. The compact and highly advanced integrated technology require this component because of its physical elasticity. The device will twist, and the circuitry will survive deformation without any effect.
Since it is quite capable of disintegrating heat, it is mainly desirable in applications where heat is inevitable. General statistics show that almost 15% of printed circuitry is flexible.
Rigid Circuit
It is also called a printed circuit board. This circuitry has a fabrication on an inflexible base layer, made of concrete, non-conductive membrane usually containing glass. It strengthens the board and stops it from distortion even under pressure.
A rigid circuit board has been in use for a substantial period now as it offers excellent sustenance for components besides impeding thermal impact. Electronic appliances that are sensibly big enough to incorporate additional features, such as different connectors, other boards and equipment integrate this device.
You can practically find them in musical instruments such as keyboards, electronic gadgets like cameras, smartphones, GPS devices, laptops and computers, and even toys. However, this type of circuitry is specifically customized for different applications because if broken anyway, the whole machine will stop working.
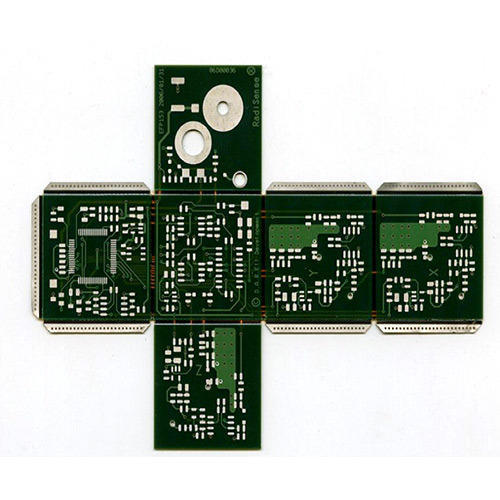
Comparison between Rigid and Flex Circuit
In reality, there are noteworthy differences between the two types in terms of framework, fabrication, and functionality. As a buyer, you need to know both the circuitries' merits and demerits before choosing the most appropriate.
Elasticity
The most crucial difference between a rigid and a flex circuit is contingent to their names. The flexible circuitry can be curved, bent, and even folded to suit the final application. If designed appropriately, it can even flex for multiple progressions without any failure. That is why we consider it the best choice for wearable electronics. The rigid circuit is inflexible, whereas flex circuit can bend or curl.
Manufacturing process
Rigid circuit requires a solder mask in its manufacturing process. The manufacturing of flex circuitry involves overlay meant for guarding the exposed circuitry of the flex circuit.
Secured and Reduced Assembly Time
The flex circuit is fit for smart wiring solutions where rigid circuitry won’t excel. Since you need little wiring for soldering, wrapping, and transmitting, flex circuitry's assembly cost also decreases and minimizes the chances of circuit failure. On the other hand, the rigid circuit needs additional wiring that may carry an additional cost.
Further, you can program the production of the flex circuit. It leads to a reduction in errors during assembly. However, the rigid circuit case connections are human-made, resulting in more chances of assembly errors.
Use of Conductive material
Since flex circuits tend to bend, they may integrate extra elastic rolled hardened copper as a conductive medium instead of using electro-deposited copper.
Cost of Manufacturing
The high adaptability of flex boards comes typically at a higher price. However, their flexible characteristics allow the engineers to fix them in compact spaces, thereby saving indirectly by reducing their products' size. Rigid circuit boards are more prevalent mainly due to their less cost. That is why manufacturers keep their costs enormously by using rigid circuit boards in conventional consumer electronics.
Enhanced Connectivity
As against the rigid circuit, the flexible circuit facilitates better connectivity between the user interface, other circuit boards, and electronic apparatuses in electronic packing. It extends connectivity in active flex applications where it needs to stretch uninterruptedly through the application's life. That is why electronic appliances such as laptops and foldable electronics use it extensively.
Design Options
The rigid circuit board is a typical form of printed circuit board that you can neither be bent nor twist. On the other hand, the flex circuit can take any shape according to its dimensions due to its extended flexibility.
The thickness of the Circuit Board
The conventional rigid circuit board can be as thin as .2mm, whereas the flex circuit board can be thinner than a paper.
Space and Weight Reduction
Since the flex circuit can twist and fold, it can decrease the weight and space up to 60 per cent.
The flexible circuit supports the shrinking of application’s dimension and weight as opposed to the rigid circuit. It is, therefore, appropriate for the compressed version of technologies that we use in compact and light-weight products. Examples are smartphones, medical devices, and other sophisticated and small consumer electronics items.
Packaging Solution
As it is possible to fold and bend the flexible circuitry easily around the corners, it can help shrink the size and weight both. Such a miniaturized three-dimensional connection and reduced number of device intersects is an excellent packaging solution for smartphones, wristwatches, and other microelectronic gadgets.
Durability
While rigid PCBs are typically thicker and reasonably robust, flex PCBs absorb shocks and vibrations much more effectively than rigid PCBs. This feature contributes directly to long-term reliability, product life, and functionality. The medical electronics, missile guidance systems, weapons, satellite, and other applications extensively Flexible circuits, thus they require excellent environmental survivability.
Reliability
The rigid circuit is hard and typically thicker than the flex circuit. The latter is shock and vibrations absorbent. It is also free from interface connections, connectors, and solder joints, etc. Due to reduce intersects, chances of potential failure are marginal in the flex circuit. Moderate mass and minor ductility of the circuit indicate better performance of the circuit.
Enhanced Resistance to Extreme Temperature and Effectiveness in High-Density Uses
Rigid circuit tends to be at risk of damage or distorting from heat, radiation, or chemicals. But Polyimide's extraordinary thermal stability benefits the flex circuit to endure extreme heat ranging from 200 to 400 degrees centigrade. Without affecting the application’s performance, the flex circuit can bear UV exposure, chemicals, and heat radiation. With such dependability, the engineers and manufacturers in various industries including oil and gas and automotive electronics prefer it over the rigid circuit.
Is Flexible Circuit Useful for Every Application?
The flex circuit board is intuitively useful, but it can never replace the rigid circuit board altogether. The main hindrance in implementing the flex board is the cost efficiency that consumer electronic products would desire. The rigid circuit board is relatively economical to manufacture and installation in a classic automatic high-volume manufacturing facility.
Naturally, the logical solution for a state-of-the-art product is one that integrates flex circuitry when required and works with concrete and dependable rigid circuit board where conceivable to maintain manufacturing and assembly overheads down.
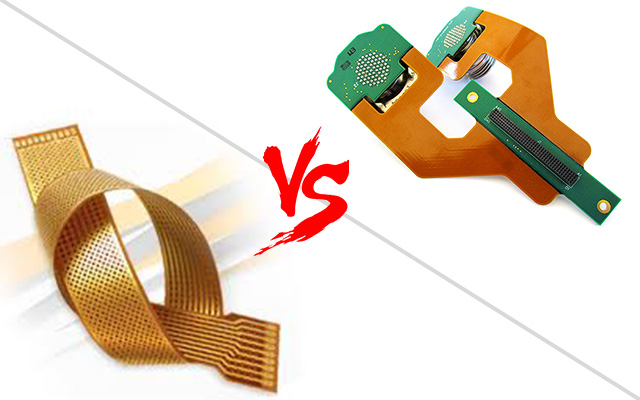
Summary
Rigid and flex circuits serve the same cause — connect different electronics and mechanical components— both the circuits have their utilities in reality. If a rigid circuit costs less, flexible circuit opens infinite rooms for blazing prospects, new product architectures and creative yet cost practical ideas.
If you analyse it more closely, you will observe that the flex circuit does not use connectors, wire binds, and other circuit boards. When such components are eliminated from the overall structure, the cost comes down. Over and above, the flex circuit offers more productivity because it is a reliable and durable product.
For More Information, Contact Us Today!




